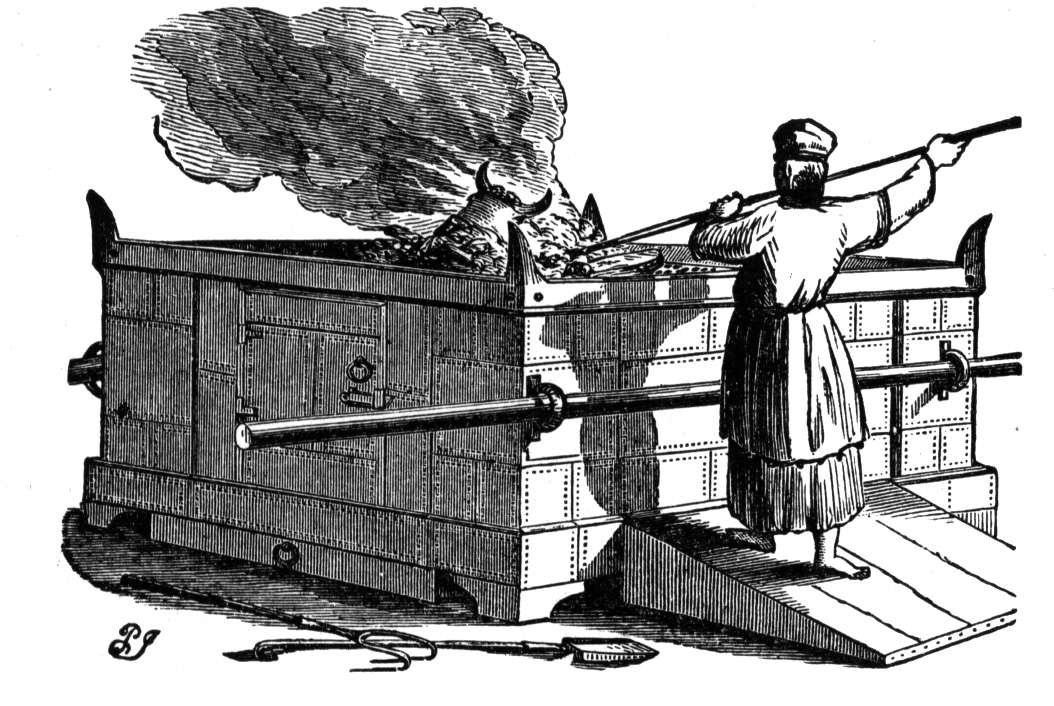
Exodus 27:1–8, An altar. Just inside the door of the tabernacle was the altar of sacrifice. It was made of acacia wood overlaid with bronze, which is a shadow picture of Yeshua bearing the judgment for men’s sins on the cross. The blood of the sacrifice was poured out on the ground at the base of the altar picturing Yeshua shedding his blood at the cross. Two lambs were offered at the altar morning and evening (Exod 29:38–42). This pictures our need to come humbly before our Father in heaven morning and evening in prayerful devotion as living sacrifices to confess our sins, to praise and thank him (Ps 51:16–17; Heb 13:15; 1 John 1:7–9).
The Altar of Sacrifice in More Details. Upon understanding that the Person and work of Yeshua is the way into life, spiritual light and truth, one must also recognize that one’s sin liability keeps one from a having personal relationship with one’s Creator. The broken fellowship with one’s Creator due to the uncleanness of sin is the reason for this. For one to have a relationship with a sinless, perfect, totally set-apart or holy Elohim,the sin problem has to be dealt with. Sin must be atoned along with the resulting guilt, shame and penalty (death) that sin brings. In the Tabernacle of Moses, liability and effect of sin is dealt with at the altar of the red heifer outside the gate of the tabernacle, which represents the work of Yeshua at the cross (Heb 13:10–13). There one was purified and made ready to come into the actual tabernacle. Upon doing so, the first thing one encountered when entering the tabernacle was the altar of sacrifice where both kosher animals and unleavened bread (made of the finest flour and the purest olive oil) were offered, and a fermented wine libation was poured out twice daily (morning and afternoon, Num 28:1–8). These all picture the body of Yeshua being broken and slain for us and our need to “eat” his body and “drink” his blood in a spiritual sense (John 6:35–58). The supper on Passover night which overlaps on to the first Sabbath of the Feast of Unleavened Bread is also picture of this since the participants would eat fire-roasted lamb, unleavened bread and fermented wine.
The fire on the altar was to be kept burning at all times; it was never to go out (Lev 6:13). Additionally, before ministering at the altar, a priest was to always wash his hands and feet at the bronze laver (Exod 30:17–21) and to put on the priestly robes (Lev 6:10). These things are prophetic shadows that point to the ministry of Yeshua before the throne of the Father in heaven. There, as our heavenly high priest, he, in an ultimate state of purity and perfection he is ever making intercession for us and reconciling us to the Father (Eph 2:18; 1 Tim 2:5; Heb 7:25–26; 8:1–2, 5–6; 9:11–22; 10:19–22; 1 John 2:1).
At the twice daily offering (the morning shacharit and the afternoon minchah), a yearling lamb was sacrificed on the north side of the altar, or its left side as viewed from the holy of holies, which represents the throne of Elohim. (Furthermore, north is significant since Scripture seems to indicate that the third heaven where Elohim dwells is in the northern region of the sky [Isa 14:13].) The lamb’s blood was then sprinkled round about the altar as an atonement for sin, while a wine libation was poured out onto the altar, and unleavened bread was cooked and offered at the same time on the altar (Num 28:1–8; Lev 1:11). The fact that the lamb was killed on the north or left side of the altar is prophetically significant since it points to Yeshua’s first coming as the Suffering Servant Messiah, the Lamb of Elohim. The left side is significant since the left hand (usually the weaker hand), in Jewish thought, represents grace and mercy, while the right hand (usually the stronger hand) represents strength, power and judgment. At his first coming, Yeshua was like a lamb led to the slaughter (Isa 52:13–53:12, especially note 53:7) as he spilled his blood as an atonement for men’s sins (Isa 53:5–6,10). Upon his death and glorious resurrection, he returned to heaven where he took his rightful place as the right arm of YHVH Elohim (Acts 7:55–56; Rom 8:34). At Yeshua’s second coming, he will come, not as a lamb led to the slaughter this time, but in power and glory as a warrior on a white stallion to judge the wicked and to reward the righteous. After that, he will assume his position as King of kings and Lord of lords over the earth during the Millennium as revealed in the Book of Revelation.
Now let’s consider the actual construction of the altar of sacrifice to see how it pointed prophetically to Yeshua in other ways. It was constructed of acacia wood overlaid in bronze. Wood and trees represent men (Ps 1:1,3; Jer 5:14). Yeshua was a carpenter. Bronze speaks of judgment. Yeshua, a man who worked in wood (representing humanity) and died on a tree took the fire of judgment upon himself for humanity’s sins.
All the animals slaughtered in the sacrificial system were similar to the minimum amount due on a credit card statement of a bill so huge one cannot possible pay the balance, so one pays the minimum until somehow, miraculously, someone will step in to pay the full amount. Yeshua paid that debt for each of us at the cross.
The first sacrifice was lit by fire from heaven. This signifies that the blood of Yeshua delivers us from the wrath of Elohim (Rom 5:9).
YHVH sent fire from heaven once to light the altar of sacrifice, but it was up to the priests to maintain that fire. The fire had to be constantly fed and the old ashes had to be removed to keep the fire burning. Similarly, when a person is redeemed spiritually and born again by the Spirit of Elohim, he has to maintain the spiritual fire in his life to ensure that it doesn’t die out due to lack of fuel, or get choked due to the ashes of traditions and dead works.
Offerings were made on the altar of sacrifice in the morning and in the evening. This teaches us that twice daily we must come before YHVH’s throne in heaven and at the altar there leave our prayers and confess our sins (1 John 1:9), drawing close to our loving Creator in communion and devotion of service to him.



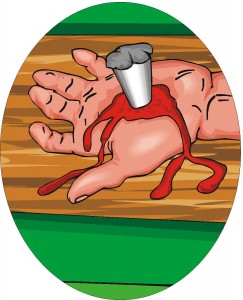 On the altar, which is a picture of the cross (Exod 24:6–8).
On the altar, which is a picture of the cross (Exod 24:6–8).