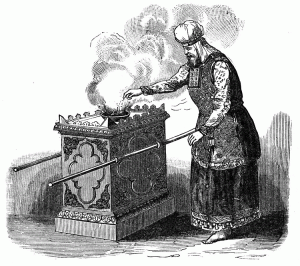
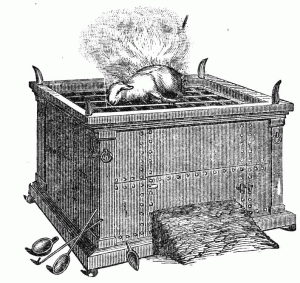
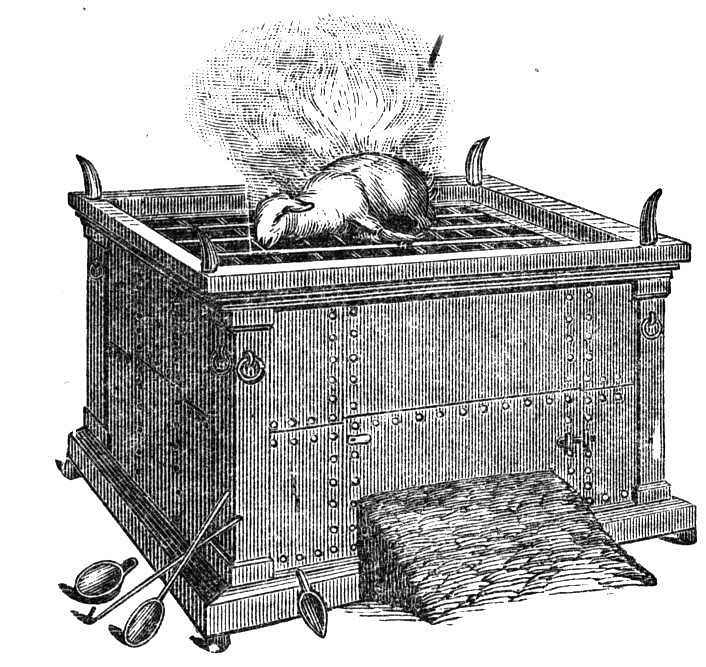
Exodus 30:1–10, Altar to burn incense. The golden incense altar was constructed of acacia wood covered in gold and was situated in front of the veil leading into the holy of holies (the most set-apart place) halfway between the menorah and the table of showbread.
Like the table of showbread, it had a golden crown around the top of it, which points to Yeshua being the head of the body of believers.
The priest burned incense on the altar twice daily, in the morning and the evening.
Scripture reveals that incense represents the prayers of the saints rising up to heaven before the throne of Elohim (Ps 141:2; Rev 5:8), which in the tabernacle is pictured by the mercy seat in the most set-apart place or oracle (d’veer). The altar of incense was a place of deep prayer, praise, worship and intercession and speaks directly to the intimate twice daily prayer life and devotions of the born-again believer before the throne of the Father in heaven.
At the altar of incense, preparation was made to enter the most set-apart place (holy Continue reading