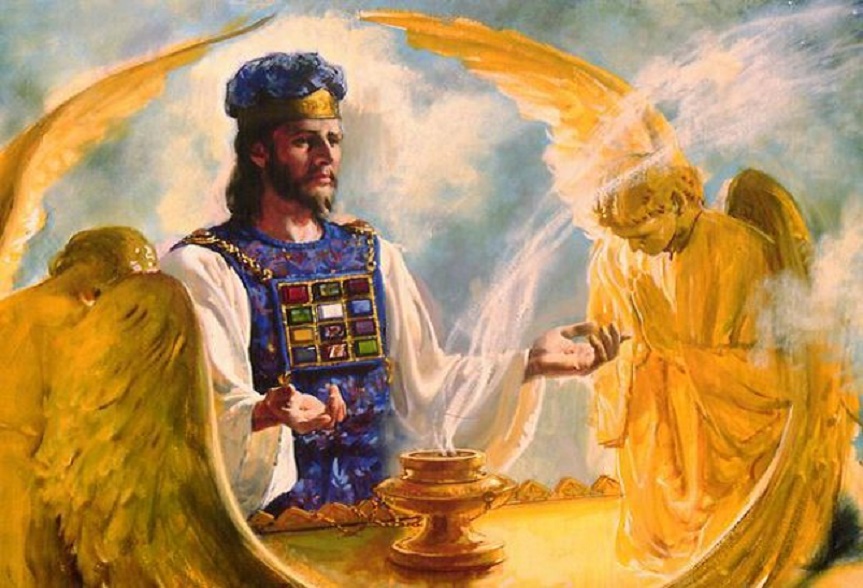
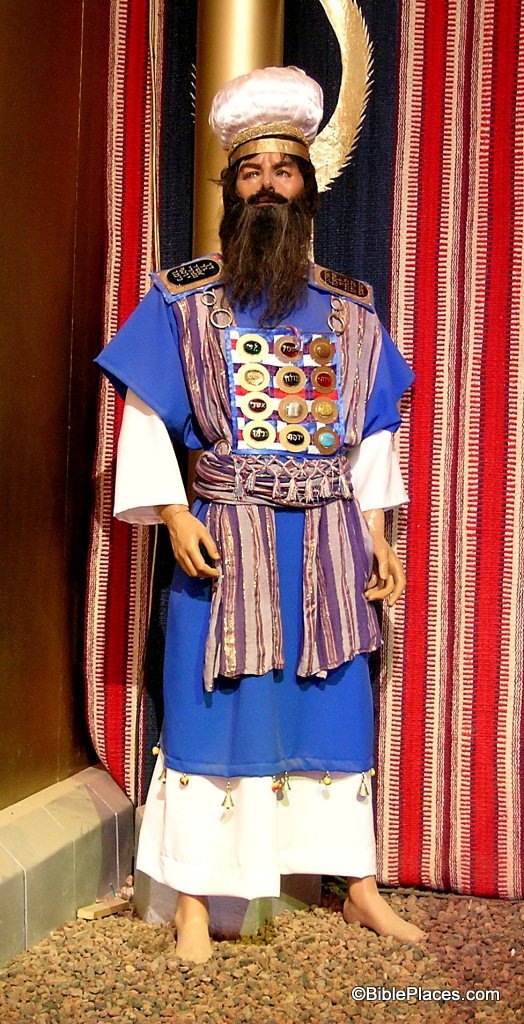
Numbers 3:11–13, I myself have taken. Here YHVH chooses the tribe of Levi instead of the firstborn male of each Israelite family to be Israel’s spiritual leaders. When the Israelites exited Egypt, YHVH chose and sanctified the firstborn male of each family to the be spiritual leader of his home in what is called the law of the firstborn (Exod 13:2, 11–16). As it had been the responsibility of the firstborn to lead his family spiritually, and, as the patriarch of his family, to pass down the family legacy and spiritual traditions to the next generation, YHVH now placed this mantle on the shoulders of the Levites. It was now their responsibility to teach the Israelites what YHVH had commanded them to do (Deut 24:8). They became the Torah teachers in Israel (Deut 33:10; Neh 8:7, 9, 13; 2 Chron 30:22) along with the priests (Lev 10:11; Mal 2:7). They were scattered throughout the land of Israel for this purpose (2 Chron 17:8–9). The reason that YHVH gave this responsibility over to the sons of Levi was because the firstborn of each family had failed to lead their families in YHVH’s paths of righteousness, and they failed to prevent the Israelites from golden calf worship (Exod 32). Only Levi remained faithful to YHVH during the golden calf incident, and thus YHVH granted them the blessing of the priestly service (Exod 32:26–29).
Originally, it had been YHVH’s intent for the entire nation of Israel to be a kingdom of priests (Exod 19:6) in order to be a light to the nations and lead the nations to YHVH and his Torah by their righteous example (Deut 4:6–8). This is why YHVH placed the land of Israel, and specifically Jerusalem, at the center of the major trade routes of the ancient world between Africa, Asia and Europe.
The Levitical priesthood (along with the elaborate tabernacle sacrificial system) was a temporary institution that YHVH added (Gal 3:19 cp. Jer 7:21–22) to the nation of Israel’s legal system because of the firstborn’s failure to prevent Israel from worshipping the golden calf idol. In a general sense, YHVH didn’t give the Israelites the Torah at this time—the principles of which they and their forefathers already had been given (e.g., Gen 26:5). So what other law was added? At Mount Sinai, the Torah was codified into a legal system (with civil penalties including the institution of a sacrificial system as a penalty for sin) and became the constitution of the nation of Israel, and YHVH also gave them the institution of the Levitical priesthood and the sacrificial system (Gal 3:19), which (along with the rest of the Torah) pointed them to Yeshua (Gal 4:16, 2). The sacrificial and Levitical systems were completely fulfilled by the Messiah as the writer of Hebrews goes into great detail to explain to us (Heb 5–11).
As already noted, it was YHVH’s intention for all Israel to become a kingdom of priests (not just the tribe of Levi) to teach the nations his spiritual truths. YHVH’s original purpose for Israel is now being fulfilled in the royal priesthood of all redeemed believers to which Peter makes reference in his first epistle (1 Pet 2:9). When the Romans destroyed the temple in Jerusalem, the Levitical priesthood along with the sacrificial system ceased to exist. This occurred some forty years after the death and resurrection of Yeshua who, at that time, became man’s sacrifice for sin once and for all and is now in heaven officiating as our Great High Priest as the writer of Hebrews reveals to us. When the temple priesthood was destroyed, YHVH’s royal priesthood of all believers was ready to take its place. In a sense, the present priesthood model defaults to the original priesthood model where the leader of each family was the priest of his home. The only difference is that the patriarchal priesthood model has been expanded and now all redeemed believers have the opportunity to become a priest in Yeshua’s eternal kingdom regardless of gender and family birth order.
Presently, the saints are preparing to be a kingdom of priest as they learn to live out and to teach others YHVH’s Torah truths. This learning process is preparing them to become kings and priests (or a kingdom of priests, Exod 19:6) in Yeshua’s millennial kingdom after his second coming where they will teach the nations the truth of YHVH (Rev 1:6; 5:10; 20:6), even as the Levites of old taught the nation of Israel YHVH’s Torah.