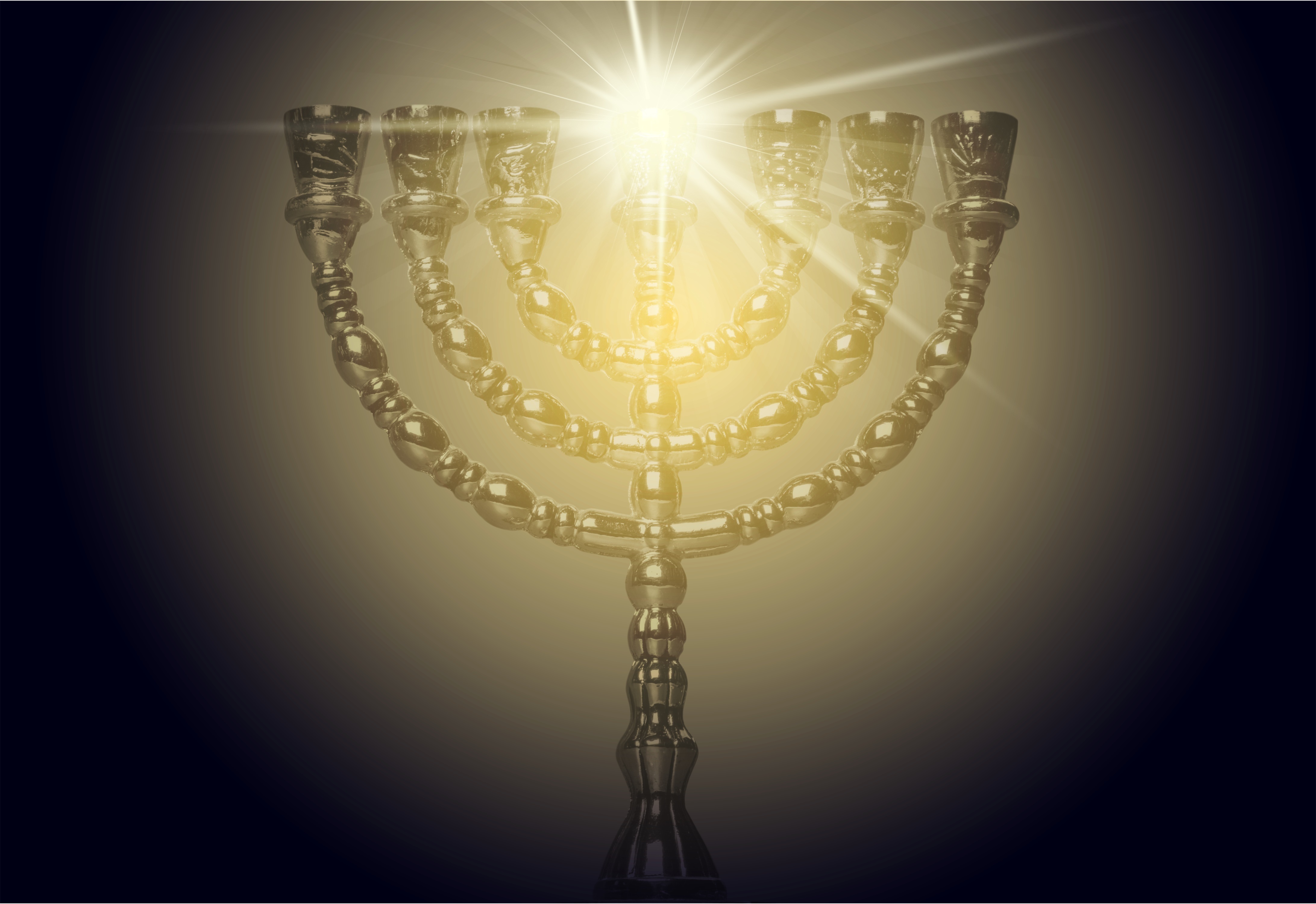
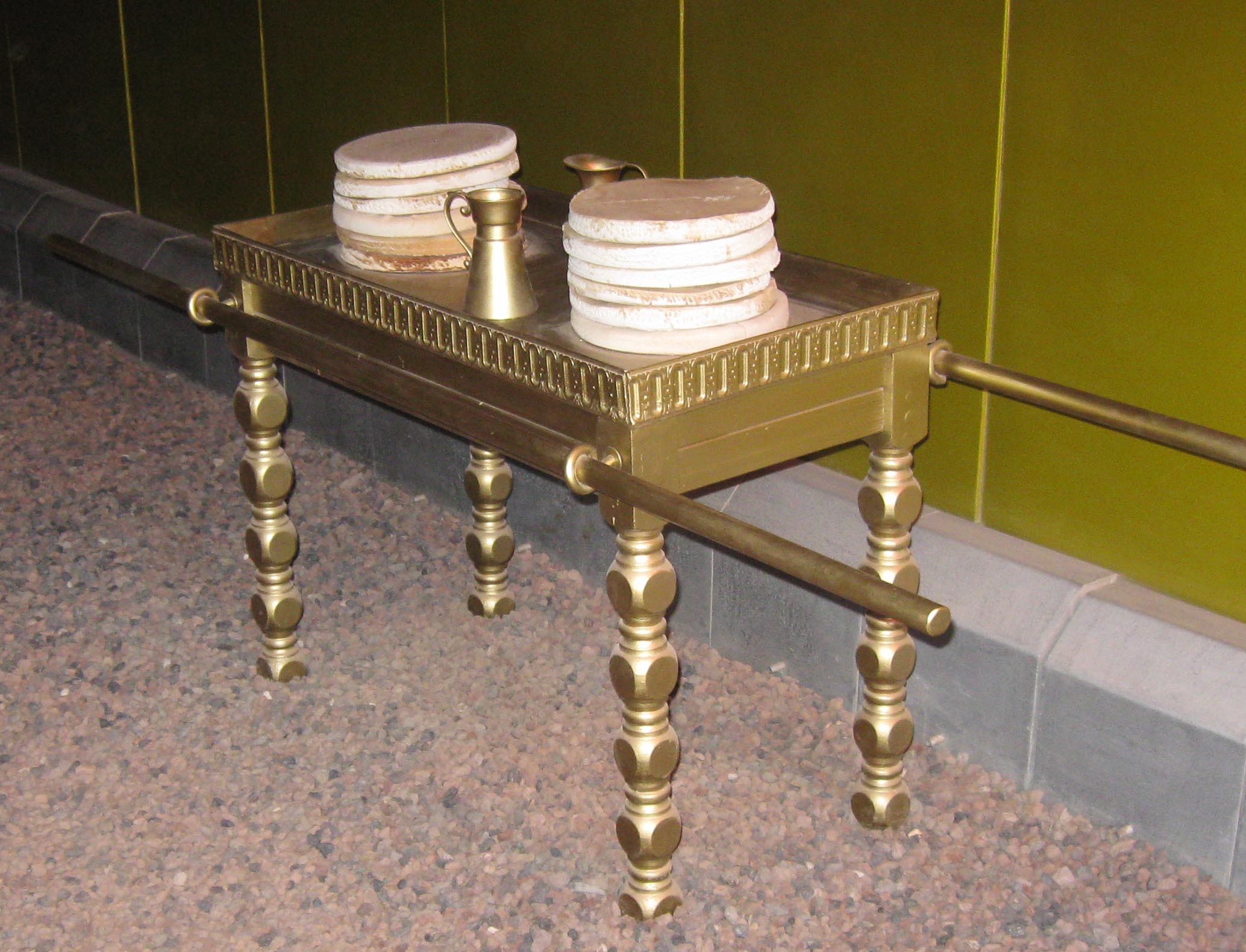
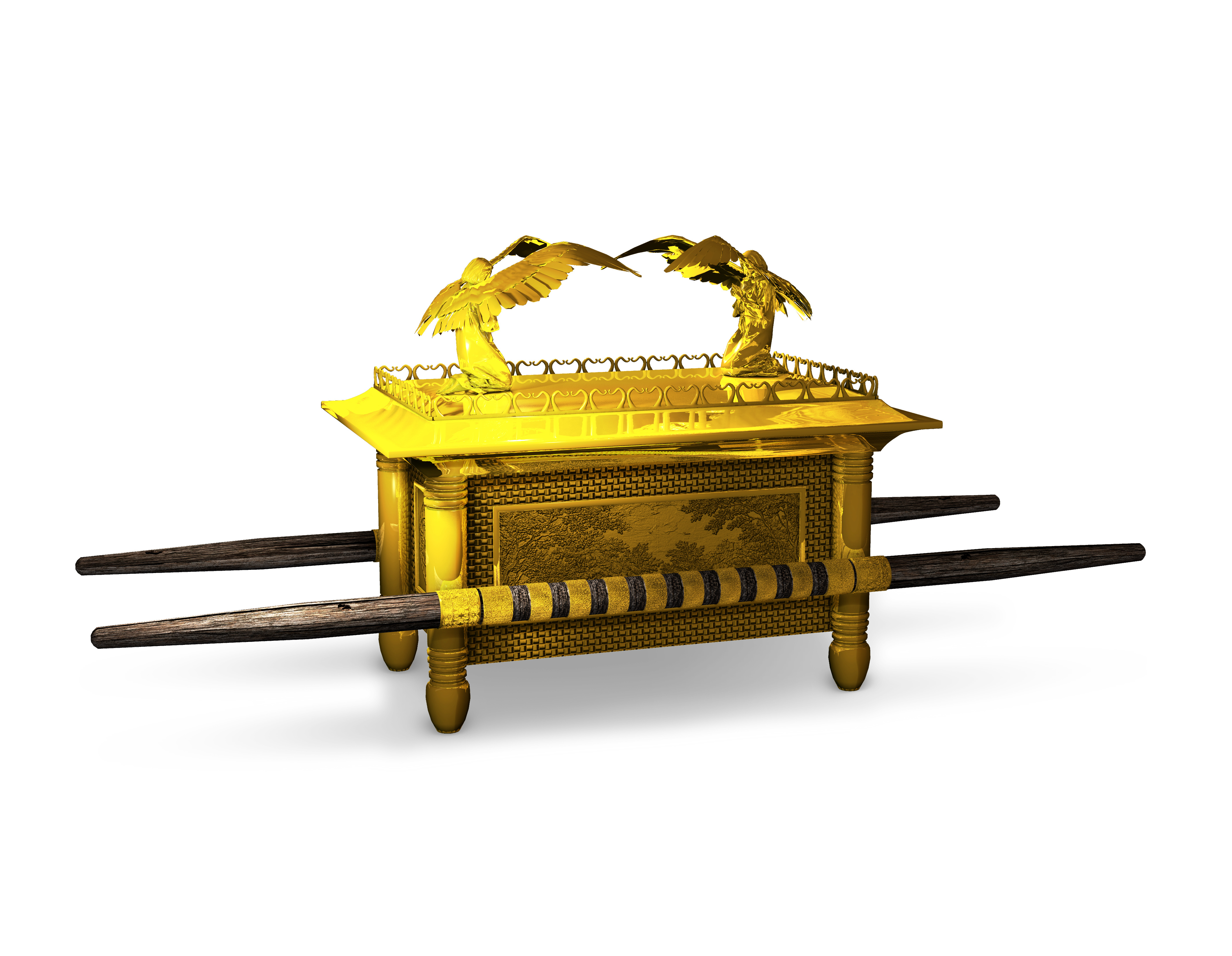
Exodus 26:31–37, A veil. The veil or parochet divided between the holy or set-apart place and the holy of holies or most set-apart place. It was woven of fine linen of the same four colors as were the previous two curtains—blue, crimson, purple and white, except this veil had cherubim embroidered into it. The most set-apart place is a picture of returning to the Garden of Eden, which had cherubim guarding its entrance (Gen 3:24), except this time it is the New Jerusalem in the New Heaven and New Earth.
It was this same veil that was rent from top to bottom in the second temple in Jerusalem at the time of Yeshua’s crucifixion (Matt 27:51). The writer of the Epistle to the Hebrews teaches a correlation between the tearing of Yeshua’s flesh on the cross and the tearing of the veil, and that this event opened the way for believers to be able to enter into the most set-apart place and to come boldly before the throne of Elohim through the shed blood of Yeshua (Heb 10:19–22 cp. 4:14–16).
The Veil in More Detail
This veil to the most set apart place (also known as the oracle or deveer) contained the four colors of the other two veils: crimson, blue, purple and white. Unlike the others, this veil had embroidered cherubim on it. It hung on four pillars of overlaid gold acacia wood. The pillars were set in bases of silver with the curtain hanging by rings of gold.
This veil is what separated men from the very Presence of Elohim. At Yeshua’s death the veil in the temple was split from top to bottom (Matt 27:51) opening the way to all into the holy of holies by and through the redemptive work of Yeshua on the cross (Heb 10:19–22).