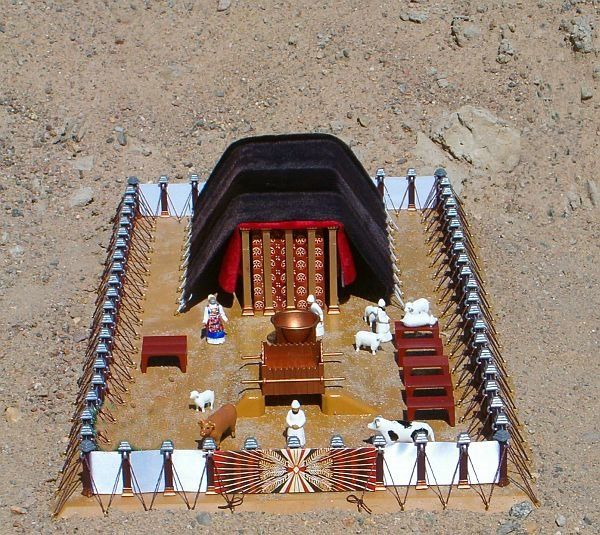

Fast Facts About the Tabernacle of Moses
The tabernacle (Heb. mishkan)was constructed circa 1450 b.c. at the foot of Mount Sinai. It took about a year to build.
Hebrew Names for the Tabernacle
- Mishkan means “tabernacle, dwelling or habitation.” Mishkan is from the root word shakan meaning “to dwell, abide, settle down, reside, tabernacle.”The word shechinah derives from shakan and refers to the manifest light or presence of YHVH among his people(Exod 25:8–9).
- Ohel (as in tent of the congregation/meeting) means “a nomad’s tent, dwelling, home, habitation”(Exod 29:42).
- Miqdash means “sacred place, sanctuary, holy place”and is from the primitive root qadash and means “to consecrate, sanctify, prepare, dedicate, be hallowed or set apart, be separate or holy” (Exod 25:8).
- Kodesh or the sanctuary because it was set-apart ( or kadosh) to Elohim (Exod 30:13).
- Ohel haeduth means “the tabernacle or tent of the testimony or witness” since it contained the ark of the covenant housing the Torah-law given to Moses, which was an abiding witness of Israel’s covenant with YHVH (Num 9:15).
- Mishkan haeduth means “tabernacle of the testimony” (Num 10:11).
Examples of YHVH Tabernacling With His People
The children of Israel have just left Egypt and are now trekking through the wilderness en route to the Promised Land. Within a couple of months, YHVH gives them their first assignment. In Exodus 25, he tells them to build a tabernacle. Why? He says to Moses, “And let them make me a sanctuary that I may dwell among them” (Exod 25:8). From the beginning of time, in the Garden of Eden, Elohim has wanted to “hang out” with man. Elohim’s desire to dwell or tabernacle with man is a theme that runs from Genesis to Revelation. We see this idea repeated in the Testimony of Yeshua (the New Testament).
John 1:14, “And the Word was made flesh and dwelt among us, (and we beheld his glory, the glory as of the only begotten of the Father,) full of grace and truth.” The word dwelt (Gr. skenoo) means “tent or tabernacle.” The Greek word skenoo most likely derives from the Hebrew word shakan meaning “to dwell, abide, settle down, reside, tabernacle”and is the root word for mishkan, which is the main name for the Tabernacle of Moses.
Luke 2:7, The baby Yeshua was laid in a “manger.” This may have been a sukkah or tabernacle, which is the flimsy little hut that Israelites build during the biblical feast of Sukkot or Tabernacles as commanded in the Torah (Lev 23:33–43). We see the connection between manger and sukkot in Genesis 33:17 where Jacob built booths (or tabernacles; Heb. succot or sukkot, sing. sukkah) for his livestock showing us that the Hebrew word sukkot can also mean “livestock barn or manger” as well as a temporary habitation where Israelites dwell during the biblically commanded festival of Sukkot. This raises the possibility that Yeshua was born in a festival sukkah during the feast of Sukkot — not just an animal barn. The LXX Greek word for sukkot in Gen 33:17 is skenas meaning “habitation, dwelling or tabernacle” and is the same word used in John 1:14 and Revelation 21:1–3 in reference to Yeshua tabernacling with his people. Putting all the pieces together, Yeshua was likely born in a sukkah-manger most probably on the Feast of Sukkot with a human sukkah (or body, of which the physical sukkah during Sukkot is a metaphorical picture) in order to redeem man from sin, so that Yeshua might tabernacle with redeemed men forever in the New Jerusalem.What an amazing Truth picture is presented before us when we put all the pieces of the puzzle together!
Revelation 21:1–3, “Now I saw a new heaven and a new earth, for the first heaven and the first earth had passed away. Also there was no more sea. Then I, John, saw the holy city, New Jerusalem, coming down out of heaven from Elohim, prepared as a bride adorned for her husband. And I heard a loud voice from heaven saying, ‘Behold, the tabernacle of Elohim is with men, and He will tabernacle with them, and they shall be His people. Elohim Himself will be with them and be their Elohim.’” The word tabernacle in verse three is skenoo in the Greek, the same word used in John 1:14.
Examples of YHVH’s People Tabernacling With Him
The talithe (also talit) or prayer shawlworn by Jewish men is an examples of YHVH’s people tabernacling with him. The word tal-ithe means “little tent.” Each Hebrew man has his own little tabernacle, tent or prayer closet to pull over his head whenever he wants to tabernacle or commune with his Elohim. When a talit is spread out with one’s arms it resembles a bird with wings. This represents YHVH’s “wings” forming a protective shield or brooding over his people. Such a place becomes a place of refuge (Ps 91:1,4). The Spirit of Elohim brooded over the waters of the earth at creation (Gen 1:2). Yeshua spoke of his desire for Jerusalem as a mother hen spreads out its wings and gathers together its young (Matt 23:37). In ancient Mideast culture, a man would cast his outer garment over his wife-to-be as an act of claiming her for marriage. In Ezekiel 16:8, YHVH spread is “wings” (Heb. kanaph meaning “edge, extremity, wings, bird’s feathered wings”) over his bride, Israel, to cover her nakedness. The Jewish wedding canopy or chuppah represents this.
Constructing the Tabernacle — All Israel Was Involved
All Israel contributed to the building of the tabernacle (Exod 25:1–7), yet YHVH chose two Israelite artisans, Bezalel and Aholiab (Exod 31:1–6), filled them with the Spirit of Elohim “in wisdom, understanding, knowledge and in all manner of workmanship…” This teaches us that the work of YHVH is a joint effort of the entire body of YHVH-Yeshua, but that YHVH will endow certain individuals with unique gifts of the Spirit in order to accomplish his specific plans and purposes (Eph 2:22; 4:11; Rom 12:4–8; 1 Cor 12 and 14).
The Israelite Encampment Around the Tabernacle
The Israelites camped around the tabernacle (Num 2:1–34). On the east side were Judah, Issachar and Zebulun; on the South side were Reuben, Simeon and Gad; on the west side were Ephraim, Manasseh and Benjamin; and on the north side were Dan, Asher and Naphtali. According to the numbers of the fighting men given in Numbers 2, we see that the encampment of Israelites around the tabernacle formed a perfect Paleo-Hebrew letter tav, which looks like a cross or our small letter t. This is amazing when added to the fact that everything in and around the tabernacle pointed to Yeshua the Messiah, to his redemptive work on the cross and the steps of each person must take to be reconciled to Elohim and eventually to inherit eternal life. Moreover, the Levites camped around the tabernacle forming a protective perimeter between the Israelites and the tabernacle itself (Num 1:53), even as Yeshua provided the five-fold ministry of apostle, prophet, evangelist, shepherd or pastor and teacher to surround the church, to edify the body of Yeshua and to bring them into the unity of the faith (Eph 4:11).
A Quick Tour of the Tabernacle
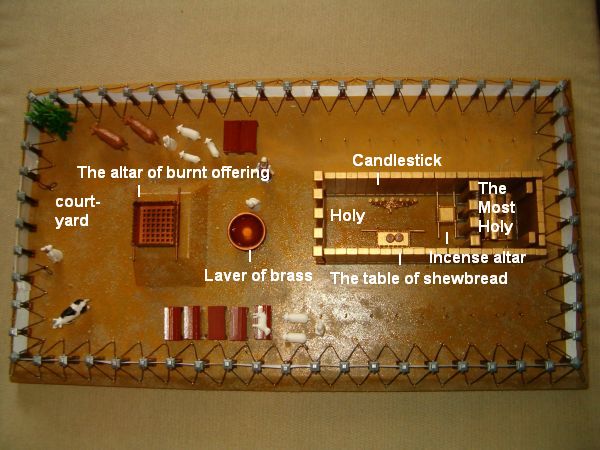
The Altar of the Red Heifer (Num 19:1–11)
See the article toward the end of this teaching on the red heifer where we discuss how it relates to Yeshua’s death at the cross. It is necessary for each saint to visit this altar representing the cross, which was located just outside the tabernacle, before being allowed into the tabernacle as the writer of Hebrews informs us (Heb 13:12–13).
The Outer Curtain (Exod 27:9–19)
The tabernacle’s outer court was approximately 150 feet long by 75 feet wide (or 11,250 square feet, which is about one-fourth of an acre) in size.
The curtains of the outer court (Exod 27:9–19) were made of fine white linen and was seven-and-a-half feet tall. The linen curtains speak of robes of righteousness the bride of Yeshua will wear on her wedding day (Rev 19:8).
Sixty pillars supported the outer curtain. They were set in heavy bronze (or brass) bases topped by silver capitals. These pillars represent redeemed humanity wearing robes of righteousness. Wood symbolizes humanity, while bronze symbolizes judgment against man because of sin, and silver represents redemption or Elohim’s ransom price for man’s sin.
The Door to the Tabernacle (Exod 27:16–17)
The door of the outer court curtain contained three colors woven into white linen fabric: blue, purple, crimson, and white. These four colors speak of different attributes of Yeshua, whom Scripture likens to the door of salvation (John 10:1–18). These four colors combine to form a full picture of Yeshua, the Redeemer and Savior of Israel. Only through him can man come to the Father, have salvation, eternal life and inhabit the glorious New Jerusalem pictured by the glory cloud over the Holy of holies in the tabernacle. The four colors also correspond to the four faces of the living beings around the throne of Elohim (Ezek 1).
Crimson symbolizes the human aspects of Yeshua, for red is the color of man and red clay from which YHVH created man (adam). Some Bible commentators believe this points to the Gospel of Mark, which reveals the nature of Yeshua at the pashat (the simpleor plain level) of biblical understanding. Some see this as corresponding to the ox cherubim and the tribe of Ephraim, which had on its banner an ox. According to Hebrew roots commentator and linguistic scholar James Trimm, “Mark presents the Messiah as the servant (the servant who purifies the Goyim in Isa 52:13, 15) the “my servant the Branch” of Zech 3:8 who is symbolized by the face of the Ox in Ezekiel 1 (the Ox being a servant, a beast of burden). Mark does not begin with an account of the birth of Messiah as do Matthew and Luke because, unlike the birth of a King, the birth of a servant is unimportant, all that is important is his work as a servant which begins with his immersion by [John]. Thus Mark’s simplified account omits any account of Yeshua’s birth or preexistence and centers on his work as a servant who purifies the [people of the nations].”
White symbolizes the righteousness of Yeshua. Some Bible commentators believe this points to the Gospel of Luke which reveals the nature of Yeshua at the remez (the hint) level of biblical understanding. Some see this as corresponding to the man cherubim and the tribe of Reuben, which had on its banner an man. Trimm writes that, “Luke wrote a more detailed account for the high priest Theophilus (a Sadducee). The Sadducees were rationalists and sticklers for details. Luke presents Yeshua as the “Son of Man” and as “the man whose name is the Branch” (Zech 6:12) who is presented as a high priest and is symbolized by the face of the man in Ezekiel 1. Luke wants to remind by remez (by implication) the high priest Theophilus about the redemption of the filthy high priest Joshua (Zech 6) and its prophetic foreshadowing of a ‘man’ who is a Messianic “Priest” and who can purify even a high priest.”
Purple symbolizes the regal or kingly aspects of Yeshua. Some Bible commentators believe this points to the Gospel of Matthew, which reveals the nature of Yeshua at the drash (the allegorical or homiletical) level of biblical understanding. Some see this as corresponding to the lion cherubim and the tribe of Judah, which had on its banner an lion. Trimm writes, “Matthew presents his account of Yeshua’s life as a Midrash to the Pharisees, as a continuing story tied to various passages from the Tanakh (for example Matt 2:13–15 presents an allegorical understanding of Hos 11:1). As a drash level account Matthew also includes a number of parables in his account. Matthew presents Messiah as the King Messiah, the Branch of David (Jer 23:5-6 and Is. 11:1f) symbolized by the face of the lion in Ezekiel 1.”
Blue symbolizes the heavenly of divine aspects of Yeshua. Some Bible commentators believe this points to the Gospel of John, which reveals the nature of Yeshua at the sod (the mystical) level of biblical understanding. Some see this as corresponding to the eagle cherubim and the tribe of Dan, which had on its banner an eagle. According to Trimm, “[John] addresses the mystical Essene sect and concerns himself with mystical topics like light, life, truth, the way and the Word. [John] includes many sod interpretations in his account. For example [John] 1:1 presents a sod understanding of Genesis 1:1. [John] 3:14; 8:28 and 12:32 present a sod understanding of Numbers 21:9 etc.” (all of Trimm’s references are from the internet site: http://www.jios.org/The%20Synoptic%20Solution_jt.html)
The Altar of Sacrifice (Exod 27:1–8)
Just inside the door of the tabernacle was the altar of sacrifice. It was made of acacia wood overlaid with bronze, which is a shadow picture of Yeshua bearing the judgment for men’s sins on the cross. The blood of the sacrifice was poured out on the ground at the base of the altar picturing Yeshua shedding his blood at the cross. Two lambs were offered at the altar morning and evening (Exod 29:38–42). This pictures our need to come humbly before our Father in heaven morning and evening in prayerful devotion as living sacrifices to confess our sins, to praise and thank him (Ps 51:16–17; Heb 13:15; 1 John 1:7–9).
The Bronze Laver (Exod 30:17–21)
The large bronze basin was fabricated from the mirrors the Israelite women donated (Exod 38:8). Perhaps James had this idea in view when he speaks of being a doer of the Word of Elohim, not just a hearer, for a hearer and not a doer is like one who sees himself in the spiritual mirror of Elohim’s Word and forgetting what he looks like does not allow the Word to transform him (Jas 1:22–25). We know that water is a poetic metaphor for YHVH’s Word (Eph 5:26; Tit 3:5; Heb 10:22; Deut 32:2).
In the laver, the priests were to wash their hands and feet before going into the tabernacle so that they would not die. The hands and feet represent the entire body since they are the highest and lowest parts of the body. They also represent our direction and our action — everywhere we go and all that we do — must be pure before ministering before YHVH.
From the Outer Court to the Inner Sanctuary
In the outer court, the theme was washing, judgment and death, while in the inner sanctuary the theme was light, food and fragrance. This represents steps of maturity in the believer’s life and progression in one’s spiritual focus. Some believers never leave the outer, for their spiritual lives never evidence the deeper values of praise, worship and abiding in YHVH characterized by the service in the sanctuary.
The Boards of the Sanctuary (Exod 26:15–30)
The walls of the tabernacle were constructed of vertical boards (20 on a side and 6 on the back) and were made of acacia wood covered in gold held sitting in silver bases. The boards were held upright by five horizontal acacia wood bars also overlaid in gold that ran the length of the walls. The boards standing tall speak of YHVH’s upright saints (Yeshurun — another name for Israel, see Deut 32:15; 33:5; 33:26; Isa 44:2) who are called to be the temple of YHVH (1 Cor 3:16; 6:19; 2 Cor 6:16) and who will also be pillars in YHVH’s eternal New Jerusalem temple (Rev 3:12). Wood overlaid with gold in silver bases speaks of redeemed humanity with the divine nature of Yeshua. It also speaks of the two-fold nature of Yeshua who was both human and divine. The five wooden bars speak of the five-fold ministry of apostles, prophets, evangelists, shepherds and teachers for the edifying or building up and perfecting of the saints — the body of Yeshua (Eph 4:11–13). Five can also speak of the five books of YHVH’s Torah —his instructions in righteousness, which shows believers how to walk uprightly before YHVH.
The Door of the Sanctuary (Exod 26:36–37)
This door had the same colors as the door to the outer courtyard (blue, crimson, white and purple) and was also woven of fine linen. The door was the same size in area, though it was a different dimension than the first door, for it was taller and narrower. This teaches us that the view of Yeshua becomes higher, and the way to the holiest place becomes narrower and the requirements become more stringent as one draws closer in proximity to YHVH’s glorious presence.
Five wooden pillars covered in gold supported by bronze bases held the curtains up. Again, the wood-covered gold speaks of the righteousness of the saints. Bronze speaks of Elohim’s judgment and five can speak of both the five books of YHVH’s Torah as well as the five-fold ministry the purpose of which is to ground YHVH’s people in his Torah-instructions in righteousness. In so doing, the Saints will become like Yeshua, who was the physical embodiment of the Torah — or YHVH’s Torah-Word made flesh (the Living Torah, John 1:1,14).
The Menorah (Exod 25:31–39)
The menorah was beaten out of a solid ingot of pure gold and stood on the left side of the holy place inside the tabernacle. It was the only light in the holy place. The menorah had seven branches with three on either side of a central stem. Each branch had three decorative cups, a knob and a flower resembling that of an almond flower. The cups were called lamps and each was filled with the purest olive oil and contained a wick that was lit. The menorah was lit each day, and each of the six outer lamps were designed so that when lit its flame pointed toward the central stem. The menorah had tools — tongs and spoons — to tend the wick. These implements were used to clean and to prepare the lamps and to remove the previous day’s ashes.
The menorah is a picture of Yeshua, the Tree of Life, who likened himself to a vine and his followers to branches” (John 15:1–7). It also pictures the idea that the saints are members of the body of Yeshua (1 Cor 12:12) and are established in him (2 Cor 1:21). His followers are connected to him, draw sustenance from him, and the spiritual light of their lives point toward him in all that they do. Believers are to be “on fire” for doing the work of Yeshua. The Spirit of Elohim directed by the Torah — both pictured by the olive oil — fuels that fire. On the Day of Pentecost, the believers in the upper room received fire of YHVH’s Spirit and had his Torah-law written in their hearts. Through the empowerment of the Spirit — both the fruits and the gifts — the saints were able take the light of the gospel out to the world. The significance of the menorah in the believer’s life is evidenced by the fact that Scripture reveals that it (not the cross) is the actual symbol for assembly of believers in Yeshua (Rev 1:12,20).
For a further discussion on the special olive oil that was used in the menorah and its spiritual significance, please read the article toward the end of this work on the subject.
The Table of Showbread (Exod 25:23–30)
On the right side of the tabernacle opposite the menorah was the table of showbread. It was constructed of acacia wood overlaid in gold, which speaks of the two-fold nature of Messiah — both human and divine, with a crown of gold, which pictures Yeshua’s being the head of the body of believers. On the table were placed twelve loaves of bread representing the twelve tribes of Israel in communion with each other and YHVH. These loaves were replaced with fresh loaves every Sabbath (Lev 25:5–9). These loaves represent the whole house of Israel fellowshipping around Yeshua, the Bread of Life. The showbread is also called the bread of presence, for the term showbread in the Hebrew literally means the bread that is “in front of, before or in the face of” Elohim.
The Golden Incense Altar (Exod 30:1–10)
The golden incense altar was constructed of acacia wood covered in gold and was situated in front of the veil leading into the holy of holies (the most set-apart place) halfway between the menorah and the table of showbread. Like the table of showbread, it had a golden crown around the top of it, which points to Yeshua being the head of the body of believers. The priest burned incense on the altar twice daily, in the morning and the evening. Scripture reveals that incense represents the prayers of the saints rising up to heaven before the throne of Elohim (Ps 141:2; Rev 5:8), which in the tabernacle is pictured by the mercy seat in the most set-apart place or oracle (Heb. d’veer). The altar of incense was a place of deep prayer, praise, worship and intercession and speaks directly to the intimate twice daily prayer life and devotions of the born-again believer before the throne of the Father in heaven.
The Veil (Exod 26:31–37)
The veil or parochet divided between the holy or set-apart place and the holy of holies or most set-apart place. It was woven of fine linen of the same four colors as were the previous two curtains — blue, crimson, purple and white, except this veil had cherubim embroidered into it. The most set-apart place is a picture of returning to the Garden of Eden, which had cherubim guarding its entrance (Gen 3:24), except this time it is the New Jerusalem in the New Heaven and New Earth.
It was this same veil that was rent from top to bottom in the second temple in Jerusalem at the time of Yeshua’s crucifixion (Matt 27:51). The writer of the Epistle to the Hebrews teaches a correlation between the tearing of Yeshua’s flesh on the cross and the tearing of the veil, and that this event opened the way for believers to be able to enter into the most set-apart place and to come boldly before the throne of Elohim through the shed blood of Yeshua (Heb 10:19–22 cp. 4:14–16).
The Most Set-Apart Place
This was the small inner-most room of the tabernacle, which contained the ark of the covenant over which the pillar of fire or glory cloud rested. Only the high priest was allowed in the most set-apart place, and only then once a year on the Day of Atonement.
The Ark of the Covenant (Exod 25:10–22)
The ark of the covenant was a small box of acacia wood overlaid in gold, which contained the golden pot of manna, Aaron’s rod that budded and the two tablets of stone containing the ten statements of Elohim — commonly called the Ten Commandments. Against the ark was leaned a scroll of the complete Torah (Deut 31:26).
Covering the ark was a golden cap called the mercy seat or kapporet and is related to the word kippur as in Yom Kippur, the Day of Atonement. Both share a common Hebrew root, which is the word kapar (Strong’s G3722), which according to the Theological Wordbook of the Old Testament (TWOT 1023)means “to make an atonement, make reconciliation, purge”) and the mercy seat — the golden “lid” covering the ark of the covenant located in the D’veer (i.e., the inner shrine of the Tabernacle of Moses) — which in Hebrew is the word kapporet was “the place of atonement or the place where atonement was made.” The TWOT defines what happened at the kapporet as follows:
“It was from the…mercy seat that [YHVH] promised to meet with the men [of Israel] (Num 7:89). The word, however, is not related to mercy and of course was not a seat. The word is derived from the root ‘to atone.’ The Greek equivalent in the LXX is usually hilasterion, “place or object of propitiation,” a word which is applied to [Messiah] in Rom 3:25. The translation ‘mercy seat’ does not sufficiently express the fact that the lid of the ark was the place where the blood was sprinkled on the day of atonement. ‘Place of atonement’ would perhaps be more expressive.”
The mercy seat covering the ark that contained the Torah is a vivid symbolic picture of YHVH’s mercy triumphing over his judgment (Jas 2:13). We all deserve death for violating his commandments, for the wages of sin is death (Rom 6:23) and sin is the violation of YHVH’s Torah commands (1 John 3:4). However. Yet when we repent of our sins and place our faith in Yeshua’s atoning death on the cross as payment for those sins, YHVH forgives us and grants us his merciful grace.
Everything in, on and around the ark pointed to Yeshua. Inside the ark was the golden pot of manna, which points to Yeshua who the bread of life — the Word of Elohim made flesh. Aaron’s rod that budded speaks of Yeshua’s role as the ultimate high priest due to his atoning and life-giving work at the cross. The two stone tablets and the Torah scroll speak of the Yeshua who was the Word of Elohim from the foundation of the world (John 1:1,14), and whose words or instructions in righteousness the saints are instructed to follow (John 14:15; 1 John 2:3–6; Rev 12:17; 14:12).
Overshadowing the mercy seat were two golden cherubim with outstretched wings. This is a picture of YHVH’s throne in heaven, which is surrounded by cherubim and other living creatures that sing his praises and minister to him (Rev 4).


The Two Pictorial Tavs (Crosses) within and over the Mishkan represent the Avrahamic and Mosaic Covenants, the Cross of Calvary represent the Messianic Covenant; Three Covenants in all.
Shalom, John